Materials and Methods
This article is a narrative review to provide a map of disease-making strategies using potential natural products to prevent and manage each stage of the disease. In the first stage, queries were performed in PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases to study articles discussing the prevention, pathogenesis, and treatment targets for COVID-19. Subsequently, each stage in prevention (preexposure and postexposure) and treatment (each of the virus- and host-directed therapies) were separately searched with keywords including “herbal,” “plant,” “natural,” and “traditional medicine” in combination with anti-viral, coronavirus, and COVID-19 to find instances of research conducted on the topic. The subject area was limited to medicine, pharmacology, toxicology, and pharmaceutics with no specific time restriction. All studies including clinical, in-vivo, in-vitro, and in-silico studies were investigated. All articles were studied to find the most robust evidences and instances of natural products on different stages. These evidences were used to find the mentioned map and strategies against COVID-19 based on the mechanism of action.
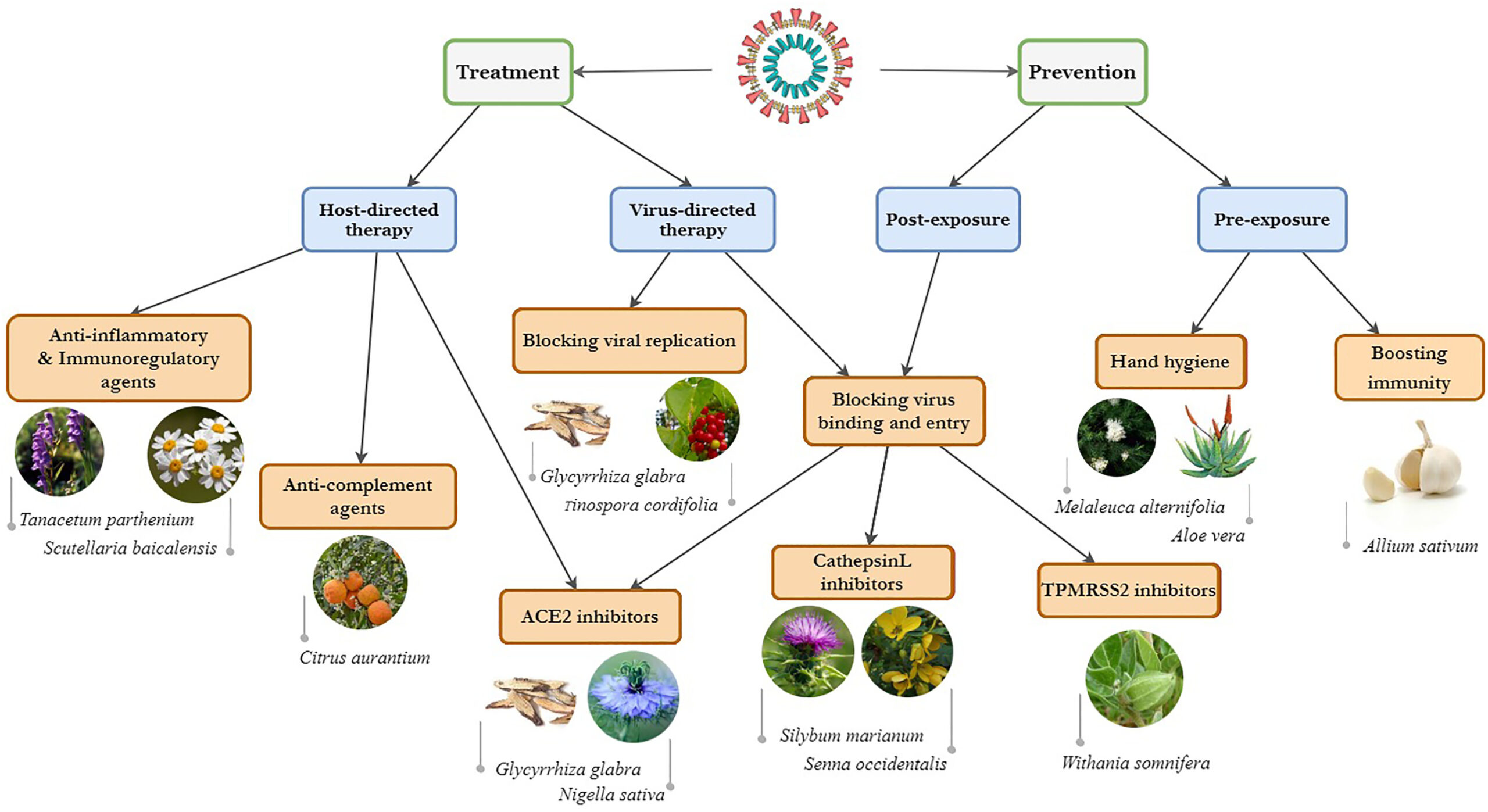
Prevention
Pre-exposure
One of the most important activities against COVID-19 is prevention. The strategy for preexposure preventive activities could be considered as one of the main first-line attempts against this disease. The strategies to find natural solutions for pre-exposure is listed in continue:
Immunomodulatory Agents
Management of individuals in the first phase of COVID-19 can encompass improving and modulating innate (monocyte, macrophage, and natural killers [NK]) and adaptive immune responses (T-cell and B-cell) by the use of immune-boosting food and herbal supplements. Prevention of virus entry and replication is crucial. The use of natural compounds may provide alternative prophylaxis by boosting the immune response in the preexposure stage. Plant-based foods enhance and help the intestinal advantageous bacteria and the overall health of the gut microbiome that makes up to 85% of the immune system of the body.
Green vegetables like broccoli (Brassica oleracea), kale or leaf cabbage, mushrooms, and plants rich in omega-3 fatty acids like flax seeds (Linum usitatissimum L.) are immunity boosters that can rapidly enhance the immune system of the elderly.
Curcumin, the main phytochemical of Curcuma longa L. has anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects, antioxidant, and potential immune-boosting properties is a potent antioxidant and stimulates the production of interferons to activate the host innate immunity. Piperine is an alkaloid compound of Piper nigrum L. that boosts innate immunity through the phosphorylation of interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF-3), type 1 interferon (IFN) mRNA, prevents lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced expression of IRF-1 and IRF-7 mRNA, and down-regulates STAT-1 activity and phosphorylation of IRF-3, type 1IFN mRNA. In a hypothesis study, garlic (Allium sativum L.) was suggested as an advantageous preventive measure before infection with SARS-CoV-2, as it suppresses the production and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and boosts immune system cells. Garlic, which has also been suggested in prophylaxis, can ameliorate symptoms in infected patients. It stimulates NK cells, lymphocytes, eosinophils, and macrophages by modulation of immunoglobulin synthesis, phagocytosis, and macrophage activation, and cytokine secretion. Also, garlic demonstrated immune system boosting capability by significantly increasing cluster of differentiation (CD4)+T cells and total white blood cell count.